User's instructions for the hot plates VTL-series,
as produced by Polymetaal.
- These hotplates are developed for the heating of metal plates
(normally copper or zinc) as used by printmakers. The warming of
the plate makes the etching ink more liquified allowing the ink to
penetrate in the etched (or engraved) grooves more easily. The
hotplate can also be easily used for the melting of "soft" or
"hard" wax on the etching plate (acid resisting substance which
covers the etching plate).
- These hotplates are not suited for melting resin powder or
asphaltum powder as used for "aquatint". The necessary temperature
is higher than these hotplates can realize. Technically it is
possible to give these hotplates a higher temperature. For the
following reasons we choose not to do so::
- For the melting of resin or asphaltum powder the necessary
temperature is between 200 to 250°C. Seen from the
legislation regarding safety standards it is unwise to make
hotplates with these high temperatures without extra and costly
safety measures.
- The necessary electrical power is much higher, therefore the
normal supply of 220 Volts is not sufficient..
- The heat transfer between the aluminium upper plate of the hot
plate and the etching plate can be irregular especially with
higher temperatures. This irregularity comes from the combination
of heat transfer through conductivity and radiation..
Polymetaal however supplies hotplates with higher temperatures in
the VTS-series.
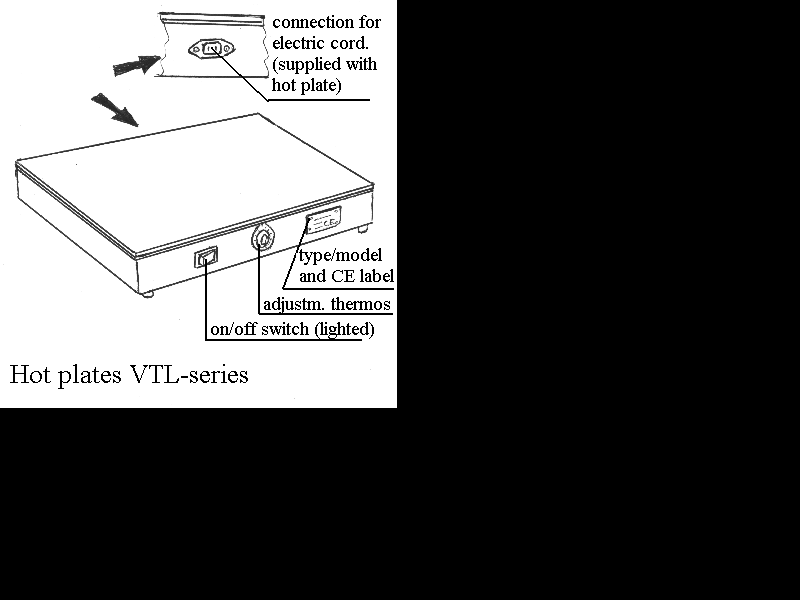
Hotplates VTL-series (see image above).
- At the back of the hotplate you will find the electric
connection to the electrical supply line. The cable is included
(3x1mm2). Ensure that the outlet has an "Earth Pen".
The construction of the outlet may vary in different countries. If
the cable plug does not fit the outlet, the plug has to be
replaced by a qualified electrician.
- The "onn/off" switch sets the electrical circuit of the
hotplate "on" and "off". When the switch is set "off" the heating
elements are turned off completely. When the switch is turned "on"
the light on the switch indicates that the hotplate is "on". When
the switch is turned "off" the switch light goes off.
- With the thermostat button the desired temperature can be set
between 30° and 110°C. By turning the thermostat button
a switch is operated connected to a liquid filled temperature
sensor which is located beneath the top of the aluminium hotplate.
Due to the construction of the thermostat (liquid based) a precise
temperature control is not possible. Electronic thermostats have a
much more precise temperature control (see hotplates VTS-series)
As soon as the hotplate, through cooling, reaches a certain
temperature (regulated by the thermostat button), the electricity
is switched back on through the thermostat. Then the full electric
power of the hotplate is used to heat up the hotplate to a certain
value, related to the position of the thermostat button. As soon
as this value is reached, the current is switched off and the
hotplate cools off until the current is switched back on. Because
of this control system there is a "pendulant" in the temperature
which causes the temperature to deviate from 5 to 10 degrees.
- The label shows the CE marking as well as model, serail
number, voltage, current and power.
- When the top plate can be hot always be careful, especially
when the switch "on" lamp is burning. Even when the hotplate is
switched "off" the top plate can remain hot so be careful.
- Do not use water in the vicinity of this equipment. Water can
lead to electrical malfunctioning of the equipment.
- This equipment does not contain any asbestos insulating
material.
NORMS AND STANDARDS
The manufacturer of these products:
Polymetaal
P.O. Box 694
2300 AR Leiden
the Netherlands
, declares that these equipment comply to the European Standard
IEC 335-1 "Safety of household and similar electrical appliances"
-and are produced according to the CE-standards (Guidelines Machinery
and Magnetic Compatibility)
-and bear the marking "CE"
Use "back-button" to go back to the
VTL-series page.